使用Hibernate搜索构建带有全文搜索的Spring Boot REST API

搜索是网络的支柱之一,而全文搜索是每个网站都需要的强制性功能之一。但是实现这样的功能是很复杂的,很多熟练的工程师已经对这个问题进行了认真的思考。所以,我们不要重新发明轮子,而要使用久经考验的Hibernate搜索库。
在这篇博文中,我们将学习如何在Spring boot中建立一个简单的REST API,并使用Hibernate Search进行全文搜索。我们将只介绍基础知识,但Hibernate Search是一个功能丰富的库,它的许多功能远远超过我们在这篇文章中所看到的。你可以在官方文档中查看它所提供的一切,https://docs.jboss.org/hibernate/stable/search/reference/en-US/html_single/#gettingstarted-framework。
创建项目
第一步是生成spring boot项目。
在本教程中,我们通过SDKman使用spring CLI,但也可以通过Web UI https://start.spring.io/ 或直接通过IDEA https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/spring-boot.html 轻松完成。
要想了解如何在自己的机器上设置CLI,请按照这个指南https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/getting-started.html#getting-started.installing.cli.sdkman。一旦你安装了CLI,执行这个命令就可以生成具有必要依赖性的项目。
spring init --dependencies=web,data-jpa,h2,lombok,validation spring-boot-hibernate-search我们打包了以下依赖项:
- 用于REST API的web依赖。
- 用于数据访问层的spring data JPA,它使用hibernate作为默认的对象关系映射工具。
- h2库,提供一个易于使用的内存嵌入式数据库。这种类型的数据库适合于像本项目这样的小型玩具项目,但它不应该被用于任何将在某个时候运往生产的正式项目。
- Lombok通过注释生成代码片段,避免任何模板代码
- validation是Hibernate对遵循JSR380规范的验证API的实现。它允许,除其他外,使用注释来验证Bean。
Hibernate搜索设置
与许多库一样,Spring Boot提供了一种简单的方法来集成Hibernate Search。我们只需要在pom.xml文件中添加所需的依赖项。
<properties>
<hibernate.search.version>6.1.1.Final</hibernate.search.version>
</properties>
...
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.search</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-search-mapper-orm</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.search.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.search</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-search-backend-lucene</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.search.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>我们使用的是hibernate search 6,这是迄今为止的最新版本,使用Lucene作为后台。Lucene是一个开源的索引和搜索引擎库,也是Hibernate Search使用的默认实现。
我们也可以使用不同的实现,如ElasticSearch或OpenSearch。
定义数据模型
第一步是定义要进行搜索的实体的模型。
作为一个例子,我们将使用一个植物实体,包含植物的俗名、学名、科和创建日期。
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
import org.hibernate.annotations.NaturalId;
import org.hibernate.search.mapper.pojo.mapping.definition.annotation.FullTextField;
import org.hibernate.search.mapper.pojo.mapping.definition.annotation.Indexed;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.Instant;
@Indexed
@Entity
@Table(name = "plant")
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class Plant {
public Plant() {
this.createdAt = Instant.now();
}
public Plant(String name, String scientificName, String family) {
this.name = name;
this.scientificName = scientificName;
this.family = family;
this.createdAt = Instant.now();
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@FullTextField()
@NaturalId()
private String name;
@FullTextField()
@NaturalId()
private String scientificName;
@FullTextField()
private String family;
private Instant createdAt ;
}让我们忽略JPA和Lombok注解,专注于Hibernate Search相关的注解。
首先,@Index注解向Hibernate Search表明,我们要对这个实体进行索引,以便对它进行搜索操作。
其次,我们用@FullTextField注解来注释我们想要搜索的字段。这个注解只适用于字符串字段,但其他字段也存在于不同类型的字段。
然后……这就是了! 对于我们这样一个简单的案例来说,就是这么简单
但是你可以用库提供的东西做得更多,比如使用条件性索引或调整索引协调。SO,如果你想了解更多,请查看官方文档。
定义数据层
我们现在需要定义我们的数据层,处理与数据库的交互。
我们使用Spring Data资源库,它围绕Hibernate的JPA实现建立了一个抽象。它在之前添加的spring-boot-starter-data-jpa依赖项中提供。
对于只需要CRUD操作的基本用例,我们可以为植物实体定义一个简单的资源库,并直接扩展JpaRepository接口。
但这对于全文搜索来说是不够的。在我们的案例中,我们希望将搜索功能添加到我们定义的所有资源库中。为此,我们需要向JpaRepository接口,或任何扩展基础Repository接口的接口添加自定义方法。
这样,我们只需声明一次这些方法,并使它们对我们项目的每个实体的每个仓库都可用。
让我们看看如何做这样的事情。
首先,我们需要创建一个新的通用接口来扩展JpaRepository接口。
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface SearchRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepository<T, ID> {
List<T> searchBy(String text, int limit, String... fields);
}我们声明将用于全文搜索操作的 searchBy 函数。
@NoRepositoryBean 注解告诉spring,这个资源库接口不应该像其他带有@Repository 注解的bean一样被实例化。
我们使用这个注解是因为这个接口的目的不是直接使用,而是由其他资源库来实现。
我们还需要为这个接口创建实现。
@Transactional
public class SearchRepositoryImpl<T, ID extends Serializable> extends SimpleJpaRepository<T, ID>
implements SearchRepository<T, ID> {
private final EntityManager entityManager;
public SearchRepositoryImpl(Class<T> domainClass, EntityManager entityManager) {
super(domainClass, entityManager);
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
public SearchRepositoryImpl(
JpaEntityInformation<T, ID> entityInformation, EntityManager entityManager) {
super(entityInformation, entityManager);
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
@Override
public List<T> searchBy(String text, int limit, String... fields) {
SearchResult<T> result = getSearchResult(text, limit, fields);
return result.hits();
}
private SearchResult<T> getSearchResult(String text, int limit, String[] fields) {
SearchSession searchSession = Search.session(entityManager);
SearchResult<T> result =
searchSession
.search(getDomainClass())
.where(f -> f.match().fields(fields).matching(text).fuzzy(2))
.fetch(limit);
return result;
}
}searchBy方法的实现是使用Hibernate搜索的地方。
以下参数被传递。
- text: 要搜索的文本
- limit:要搜索的元素的最大数量
- fields:要搜索的所有字段的名称。
我们利用java的varargs来传递我们要搜索的所有字段。
在这里,我们使用一个简单的模糊算法作为全文匹配算法,但我们可以很容易地使用自定义分析器进行更复杂的搜索。
从现在开始,需要全文搜索的资源库只需要实现SearchRepository接口,而不是Spring提供的标准JpaRepository接口。
而这正是我们为植物实体所做的事情。
package com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.repository;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model.Plant;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface PlantRepository extends SearchRepository<Plant, Long> {
}正如你所看到的,所有的实现都已经完成了,我们只需要实现之前创建的SearchRepository接口就可以访问SearchRepositoryImpl类中定义的实现。
最后一步是向Spring指明使用SearchRepositoryImpl作为基类来检测Jpa仓库。
package com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.repository.SearchRepositoryImpl;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(repositoryBaseClass = SearchRepositoryImpl.class)
public class ApplicationConfiguration {
}请注意,由于我们没有指定任何基础包来搜索,Spring将使用定义了该配置的包作为基础包。
定义业务层
现在让我们使用我们刚刚定义的数据层,通过声明一个服务来创建业务代码。
package com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.service;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model.Plant;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.repository.PlantRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class PlantService {
private PlantRepository plantRepository;
private static final List<String> SEARCHABLE_FIELDS = Arrays.asList("name","scientificName","family");
public PlantService(PlantRepository plantRepository) {
this.plantRepository = plantRepository;
}
public List<Plant> searchPlants(String text, List<String> fields, int limit) {
List<String> fieldsToSearchBy = fields.isEmpty() ? SEARCHABLE_FIELDS : fields;
boolean containsInvalidField = fieldsToSearchBy.stream(). anyMatch(f -> !SEARCHABLE_FIELDS.contains(f));
if(containsInvalidField) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
return plantRepository.searchBy(
text, limit, fieldsToSearchBy.toArray(new String[0]));
}
}我们告诉Spring,这个Bean是应用程序业务层的一部分。
它包含一个searchPlant函数,转发对SearchRepository的searchBy函数的调用。
在转发调用之前,它验证了所提供的字段。
这些字段被列入白名单,以检查搜索将只针对所需的字段,也就是我们之前用@FullTextField注解标注的字段。
如果提供的字段之一不在白名单中,我们会抛出一个IllegalArgumentException。为了简单起见,我们没有处理这个异常,但应该使用spring提供的许多处理异常的方法中的一种来正确处理它。
定义网络层
下一步是定义REST API来接收来自客户端应用程序的HTTP请求。
package com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.controller;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model.Plant;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model.SearchRequestDTO;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.service.PlantService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/plant")
public class PlantController {
private PlantService plantService;
public PlantController(PlantService plantService) {
this.plantService = plantService;
}
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<Plant> searchPlants(SearchRequestDTO searchRequestDTO) {
log.info("Request for plant search received with data : " + searchRequestDTO);
return plantService.searchPlants(searchRequestDTO.getText(), searchRequestDTO.getFields(), searchRequestDTO.getLimit());
}
}我们使用一个基本的Rest控制器和一个单一的GET映射。在将调用转发到业务层之前,我们记录事件以追踪请求的接收情况,以方便对应用程序的监控。
它使用一个SearchRequestDTO来接收搜索请求
package com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class SearchRequestDTO {
@NotBlank
private String text;
private List<String> fields = new ArrayList<>();
@Min(1)
private int limit;
}它是一个简单的POJO,包含用于搜索的参数。我们再次使用Javax Bean Validation注解来确保请求的有效性,以及Lombok @Data注解来生成模板代码(Getters, Setters, toString(), …)。
请注意,通过使用POJO作为REST API端点的单一参数,我们希望客户端在HTTP请求中把这些参数作为Request Parameter发送。
对数据进行索引
最后,为了让Lucene能够在数据中进行搜索,它需要被编制索引。
在运行时,索引由Hibernate自动管理,在每次通过Hibernate ORM执行操作(如创建或删除一个实体)时应用变化。然而,我们仍然需要为已经存储在数据库中的数据初始化索引,如果有的话。
为了这个目的,我们需要在application.yml文件中添加一些配置。
server:
port: 9000
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:mydb
username: mozen
password: password
jpa:
open-in-view: false
properties:
hibernate:
search:
backend:
type: lucene
directory.root: ./data/index我们指出存储Lucene索引的根目录。在这里,我们选择直接把它放在项目文件夹中,但在生产中运行时,这个目录应该仔细选择,这取决于你的应用程序被部署在哪里。
我们还创建了一个组件来包装所有与Lucene索引有关的操作。
package com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.index;
import org.hibernate.search.mapper.orm.Search;
import org.hibernate.search.mapper.orm.massindexing.MassIndexer;
import org.hibernate.search.mapper.orm.session.SearchSession;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
@Transactional
@Component
public class Indexer {
private EntityManager entityManager;
private static final int THREAD_NUMBER = 4;
public Indexer(EntityManager entityManager) {
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
public void indexPersistedData(String indexClassName) throws IndexException {
try {
SearchSession searchSession = Search.session(entityManager);
Class<?> classToIndex = Class.forName(indexClassName);
MassIndexer indexer =
searchSession
.massIndexer(classToIndex)
.threadsToLoadObjects(THREAD_NUMBER);
indexer.startAndWait();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IndexException("Invalid class " + indexClassName, e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IndexException("Index Interrupted", e);
}
}
}对于我们的简单演示应用程序,我们只声明了一个函数,该函数在过程中使用指定数量的线程为给定的Class建立索引。
我们现在需要通过先前定义的Plant类作为参数调用该函数。
为此,我们还可以创建一个新的REST控制器,包含一个端点,通过HTTP请求来触发索引,以便能够随意重建索引。
但在本文中,我们只是要使用一个ApplicationRunner,它将在每次启动时被调用。
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner buildIndex(Indexer indexer) throws Exception {
return (ApplicationArguments args) -> {
indexer.indexPersistedData("com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model.Plant");
};
}
}我们在主应用程序类中直接定义Bean。
buildIndex方法通过依赖注入将索引器作为一个参数。该方法在应用程序启动时执行(就在上下文初始化之后和spring boot应用程序启动之前)。
把它们放在一起
让我们首先初始化样本数据。
package com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.index.Indexer;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model.Plant;
import com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.repository.PlantRepository;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner initializeData(PlantRepository plantRepository) throws Exception {
return (ApplicationArguments args) -> {
List<Plant> plants = Arrays.asList(
new Plant("subalpine fir", "abies lasiocarpa", "pinaceae"),
new Plant("sour cherry", "prunus cerasus", "rosaceae"),
new Plant("asian pear", "pyrus pyrifolia", "rosaceae"),
new Plant("chinese witch hazel", "hamamelis mollis", "hamamelidaceae"),
new Plant("silver maple", "acer saccharinum", "sapindaceae"),
new Plant("cucumber tree", "magnolia acuminata", "magnoliaceae"),
new Plant("korean rhododendron", "rhododendron mucronulatum", "ericaceae"),
new Plant("water lettuce", "pistia", "araceae"),
new Plant("sessile oak", "quercus petraea", "fagaceae"),
new Plant("common fig", "ficus carica", "moraceae")
);
plantRepository.saveAll(plants);
};
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner buildIndex(Indexer indexer) throws Exception {
return (ApplicationArguments args) -> {
indexer.indexPersistedData("com.mozen.springboothibernatesearch.model.Plant");
};
}
}我们用第二个Bean声明来扩展主应用程序类。它将以与第一个相同的方式在应用程序启动时运行。
请注意,我们没有在任何地方声明数据SQL模式。因为我们的数据库是嵌入式数据库,spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto属性默认设置为creative-drop,我们的数据库模式是自动生成的,这对于像这样的简单应用来说是很好的。
现在,让我们测试一下,首先启动我们的应用程序。
mvn spring-boot:run有多种方法来测试搜索端点。
我们可以使用API平台的Postman。
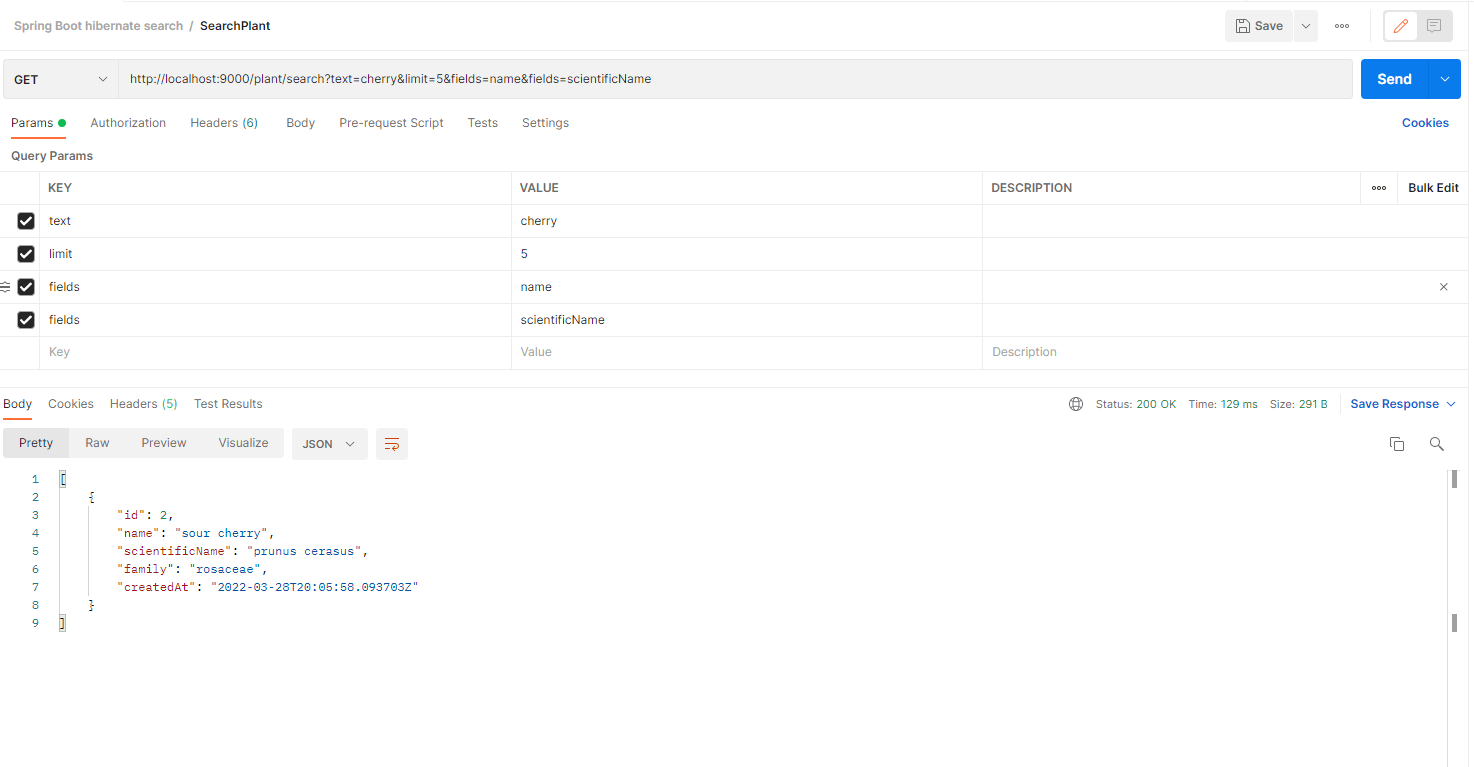
或者我们可以使用一个简单的cUrl命令,加上所需的参数。
// Search in all fields
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9000/plant/search?text=cherry&limit=5'
// Search only in specified fields
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9000/plant/search?text=sian p&limit=5&fields=name&fields=scientificName'就这样了! 我们现在已经通过HTTP端点实现了全文搜索。
正如我在这篇博客中多次提到的,Hibernate搜索提供了更多的功能,而我们在这里只是浅尝辄止而已。